Post Activity
 747
747
Table of Content
Share This Post
Table of Content
Managing the decentralized network of smart grid systems is complex. AI in smart grid management makes it possible to process massive amounts of data in real time.
It helps utilities make fast, informed decisions. With technologies like machine learning and neural networks, AI acts as the brain of the modern power grid. It improves reliability, detects faults early, and ensures better energy use across homes, cities, and national infrastructure.
The Role of AI in Smart Grid Systems
Smart grid systems introduce two-way communication and integrate Distributed Energy Resources (DERs), such as solar panels and wind turbines. However, the complexity of managing this decentralized system requires intelligent energy management systems. AI enables dynamic, data-driven decision-making across electric grids. It also harnesses machine learning, neural networks, and deep learning. As a result, it serves as the brain of modern electricity grid operations, playing a crucial role in grid stability and fault detection. Here’s how AI optimizes smart grid systems:
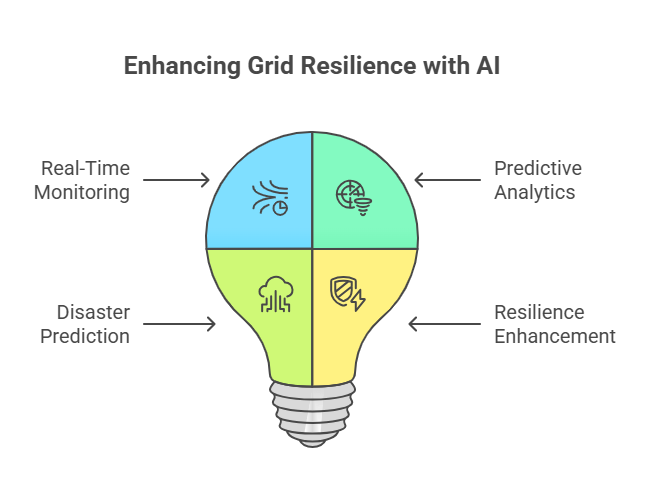
Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Analytics
AI algorithms ingest vast amounts of real-time data from Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, and IoT-enabled sensors. These smart grid applications monitor consumption, energy production, voltage fluctuations, and asset health.
Disaster Prediction and Resilience
Extreme weather conditions pose an increasing threat to grid performance. AI enhances disaster resilience through predictive control and real-time simulation. Intelligent forecasting models simulate weather scenarios and their impact on infrastructure. These tools support self-healing capabilities in microgrid energy management, rerouting control signals, and initiating islanding protocols to ensure a consistent energy supply. Energy tech startups and affiliated organizations are actively deploying AI-enhanced smart grid integration platforms for disaster-prone regions, especially across the United States.
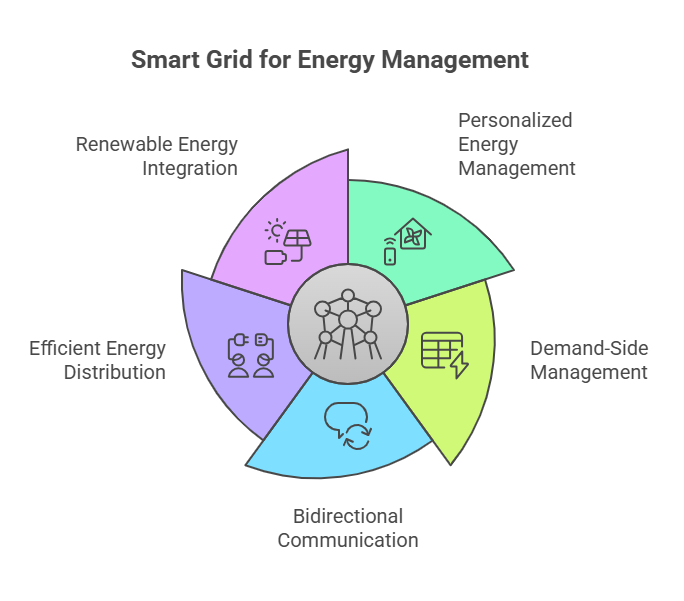
Personalized Energy Management and Household-Level Optimization
On the consumer front, smart grid technology enables personalized energy management. Consequently, AI-driven platforms optimize the operation of household systems like air conditioners, lighting, and electric vehicles. Through demand-side management and load forecasting, users receive insights to reduce energy bills and their carbon footprint.
Enhancing Grid Efficiency and Sustainability
Efficient energy distribution is central to a sustainable future. AI coordinates power distribution in real time. This aligns renewable energy generation with energy consumption patterns. Furthermore, Reinforcement Learning (RL) supports demand management and Load Flow Analysis under changing conditions. This ensures seamless integration of non-conventional energy sources and reduces dependency on fossil fuels.
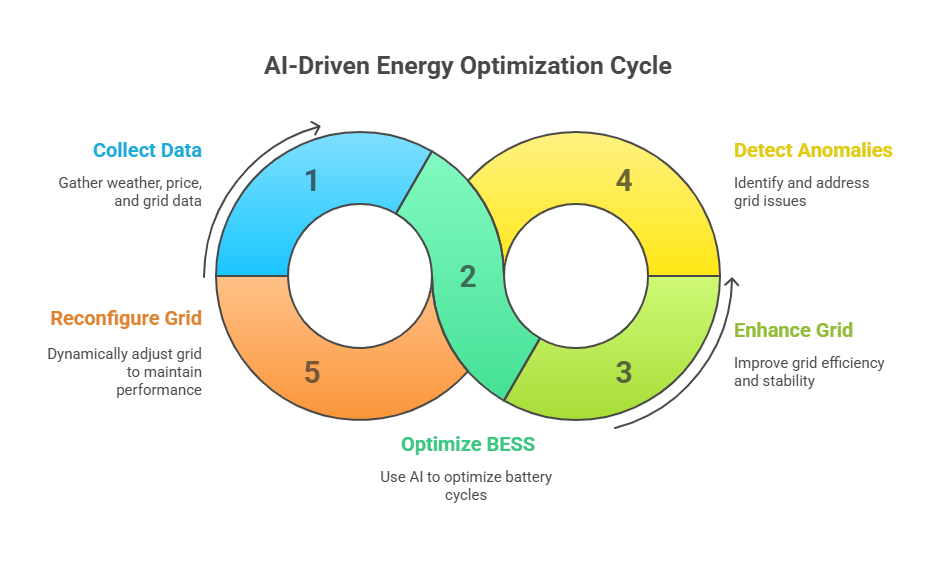
Energy Storage Optimization
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are critical for renewable energy integration. AI models optimize charge-discharge cycles based on weather forecasts, electricity prices, and the flow of electricity. These control technologies support energy storage systems that maximize grid efficiency. It also reduces excess energy curtailment and maintains operational efficiency.
Streamlined Energy Distribution
AI enhances distribution grid management through topology mapping, anomaly detection, and linear regression-based analysis. By detecting load imbalances and voltage issues, smart grids can dynamically reconfigure to maintain electrical grid performance.
Thinking of Outsourcing?
Access a wide range of outsourcing companies and find your best fit.
Empowering Consumers through AI and Smart Home Technologies
Smart home technologies, powered by Generative AI and intelligent automation, let grid operators engage directly with consumers. By integrating with smart thermostats and appliances, these systems:
- Respond to dynamic tariffs.
- Support energy transition objectives.
- Reduce peak loads.
Customer engagement is further improved by real-time alerts, usage visualizations, and gamified energy challenges.
Consumer Education and Engagement
Educating end-users is pivotal to optimized energy management. AI applications personalize education content tailored to user behavior.
This knowledge base fosters a more informed public on the roles of cyber-physical systems and energy management systems. Transparent communication technologies build trust and promote active participation in demand response programs.
Bridging Energy Distribution Gaps
AI-enabled mapping and prioritization help identify regions with insufficient infrastructure. Remote sensing technologies and Transfer Learning models streamline infrastructure investments. These tools are vital for enabling the integration of hydrogen energy and renewable energy production in isolated areas.
Facilitating Energy Management at All Levels
From national grids to building-level systems, AI plays an important role in optimizing energy management. Governments, utilities, and building managers can implement predictive analytics, enhancing grid resilience and energy efficiency.
Ready to Build Your Team?
Let’s create together, innovate together, and achieve excellence together. Your vision, our team – the perfect match awaits.
Challenges and Considerations
AI’s Energy Footprint
AI in smart grid management, while beneficial, has its own carbon emissions. The training of large-scale models consumes significant energy and needs greener approaches.
Lightweight models, edge AI, and optimized data pipelines can mitigate this impact.
Smart Grid Security
Digital technologies elevate cybersecurity threats. Robust cybersecurity measures are needed to counter unauthorized access, data poisoning, and anomaly detection gaps. Advanced intrusion detection systems and encryption tools are the anchor of smart grid security.
Infrastructural Constraints
Legacy systems often lack interoperability with digital smart grid environments. As a result, upgrades require financial investment, technical alignment, and regulatory coordination.
Cross-industry forums, academic collaborations, and open-access publications can accelerate innovation and foster best practices.
Future Outlook
- Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: Future AI developments will focus on optimizing AI models for wind, solar, and green hydrogen contexts.
- Advancements in Metering Infrastructures: New generations of smart meters and communication systems offer higher-resolution data and quicker response times. This will improve forecasting accuracy, enhance power grid automation, and foster efficient demand-side operations.
Conclusion
AI in smart grid management is redefining the energy industry. AI supports a sustainable energy future and ensures efficient energy distribution, predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and personalized usage. The integration of artificial intelligence across the electrical grid enables a smarter, more resilient, and democratized energy ecosystem for generations to come.
Find Your Perfect Software Outsourcing Partner
Unlock a world of trusted software outsourcing companies and elevate your business operations seamlessly.